Herniated Disc Recovery Time According to the Medical Literature
Herniated disc recovery time varies and involves pain relief in addition to decreased disc herniation size on imaging.
The medical literature shows that herniated disc pain typically lasts anywhere from 6 to 12 weeks. So a month and a half to three months.
The pain goes away long before the disc is completely healed. This is good news. You don’t have to suffer for an entire year until the disc heals.
It’s important to understand the time it takes for your disc to heal though. Even though you’re not having lower back pain after several months it’s still important to move and exercise in ways that promote disc health and healing.
How long does it take for a herniated disc to heal?
Like all biological tissues, there is a wide variance in healing time of lumbar discs. The medical literature states that herniated discs take anywhere from 5 to 22 months to heal. The average is 13 months, so right around 1 year.
What constitutes healing?
Regression or healing of a disc in the medical literature is defined as an MRI that shows no disc herniation where there was a herniation. It’s important to remember that herniated lumbar discs can be asymptomatic. So there does not have to be a complete regression of a herniated disc to be pain-free.
This brings us to the next question.
How do herniated discs heal?
Discs heal through a process termed spontaneous regression. Herniated discs are more likely to undergo spontaneous regression when they’re more severe.
A disc that is completely extruded or sequestered has the best chance of spontaneous regression. This is good news. The worse the herniation is the greater likelihood your body will take care of it naturally.
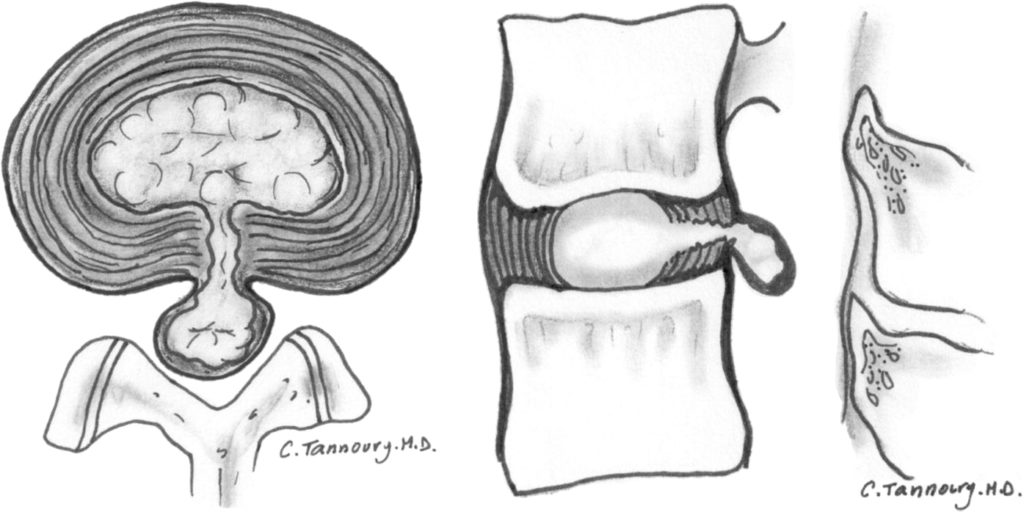
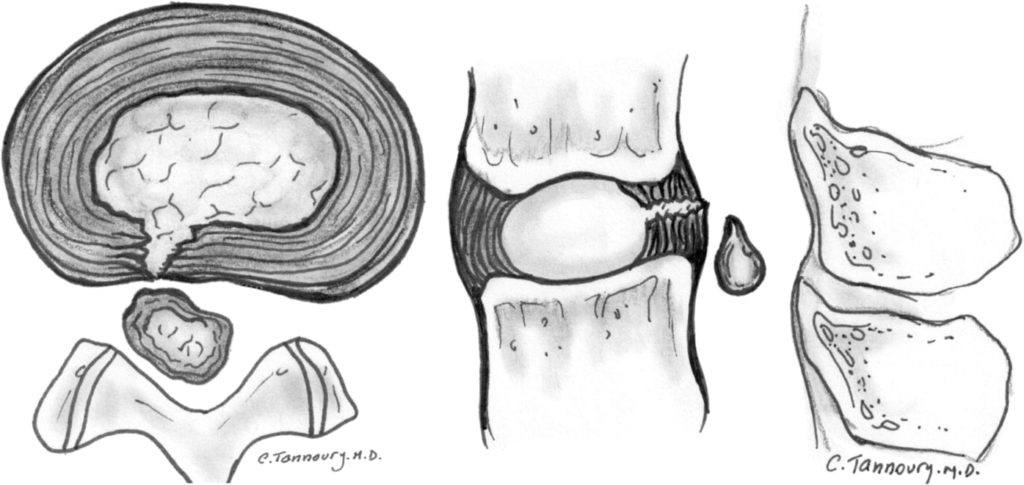
When a disc herniates the inner part (the nucleus pulposus) pushes out through the annulus fibrosus (outer part of the disc). If the inside is pushed completely out ( disc extrusion) or pushed out and part breaks off (sequestered disc herniation) there is a good chance spontaneous regression will occur.
With smaller disc herniations spontaneous regression happens, just less frequently.
The three theories describing how spontaneous regression happens
- The herniated piece of nucleus pulposus dehydrates and shrinks.
- The posterior longitudinal ligament pushes the herniation back into the disc.
- There is an inflammatory and autoimmune response that basically cleans up the extruded nucleus pulposus.
It is likely that each of these proposed theories play a role in the healing of a herniated disc. In some cases each method of spontaneous regression could play a role.
With the more severe disc herniations that result in sequestered disc material into the epidural space it’s likely that an inflammatory and autoimmune response is at work. It’s also likely that part of the disc material does dehydrate and shrink.
With a less severe disc herniation that does not result in sequestered nucleus pulposus the posterior longitudinal ligament could push the herniation back in to a degree.
Discs Heal
The take home message is; DISCS HEAL.
The more severe the herniation the more likely spontaneous regression is. Even if you have a disc herniation that doesn’t completely resolve on MRI you can still be pain-free.
It’s likely your body does not completely heal small disc herniations because they are normal and not problematic.
How Herniated Discs Heal covers the spontaneous regression process and the likelihood that it will happen.
Three Simple Ways to Heal Bulging Discs describes three principles that will decrease forces through your lumbar discs. Less force through your discs translates to less pain and healing.
If your symptoms are related to a herniated disc stay away from these types of exercises.
Herniated Disc Recovery Time Recap
Based on the medical literature herniated disc related pain tends to last for 6 to 12 weeks. Disc herniation size may decrease over time, although the herniation or bulge may remain unchanged. When the size of the disc herniation does decrease there is a wide range in the time it takes for this to occur, 5 to 22 months. The average is 13 months.
As outlined in this article, specific exercise training, movement pattern training, and avoiding lumbar flexion oriented exercises facilitate the recovery process.
FAQs
Herniated disc pain typically lasts 6 to 12 weeks. According to the medical literature herniated discs take 5 to 22 months to heal. The average is 13 months.
The pain from a herniated disc typically lasts 6 to 12 weeks. Based on the medical literature herniated discs take 5 to 22 months to heal. The average is 13 months. Healing in the medical literature is defined by a herniated disc regressing in size or regressing completely. So on MRI the herniated disc would be smaller, or gone completely. This does not always happen though. Many herniated discs remain visible on MRI though are not painful.
References
Altun I, Yüksel KZ. Lumbar herniated disc: spontaneous regression. Korean J Pain. 2017;30(1):44‐50. doi:10.3344/kjp.2017.30.1.44
Fardon DF, Williams AL, Dohring EJ, Murtagh FR, Gabriel Rothman SL, Sze GK. Lumbar disc nomenclature: version 2.0: Recommendations of the combined task forces of the North American Spine Society, the American Society of Spine Radiology and the American Society of Neuroradiology. Spine J. 2014 Nov 1;14(11):2525-45. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2014.04.022. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Review. PubMed PMID: 24768732.