The erector spinae musculature is located along the right and left sides of the spinal column, and runs the entire length of the spine. The muscle complex functions primarily to extend, side bend, and stabilize the spine.
The muscles can be subdivided into the superficial and deep portions. The attachment points and function differ between the superficial and deep ES (erector spinae).
Superficial Erector Spinae
Superficial to Deep, Starting at the Skin
- Skin
- Thoracolumbar fascia
- Erector spinae aponeurosis
- Deep erector spinae
- multifidus
The superficial ES is the first muscle underneath the thoracolumbar fascia. It connects to the erector spinae aponeurosis and travels superiorly (upward) to attach to the ribs and thoracic spine.
The medial (inside part closest to the spine) part of the ES is called the longissimus thoracis.
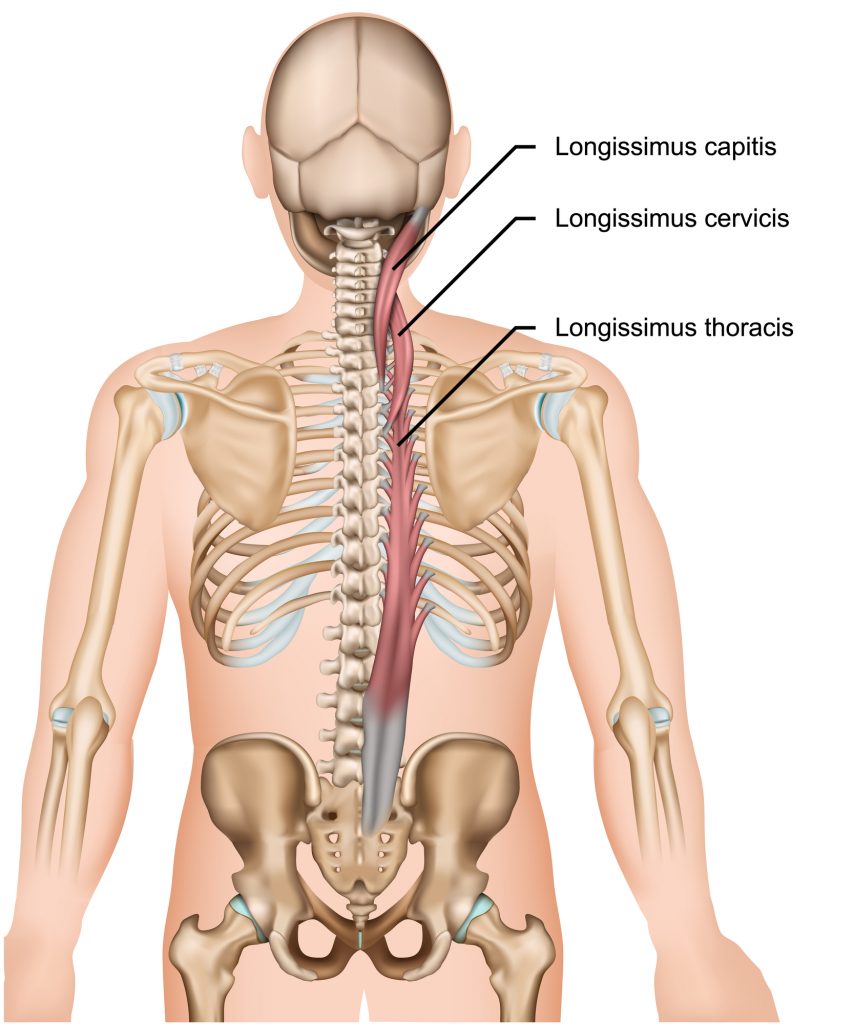
The lateral ES is known as iliocostalis lumborum.
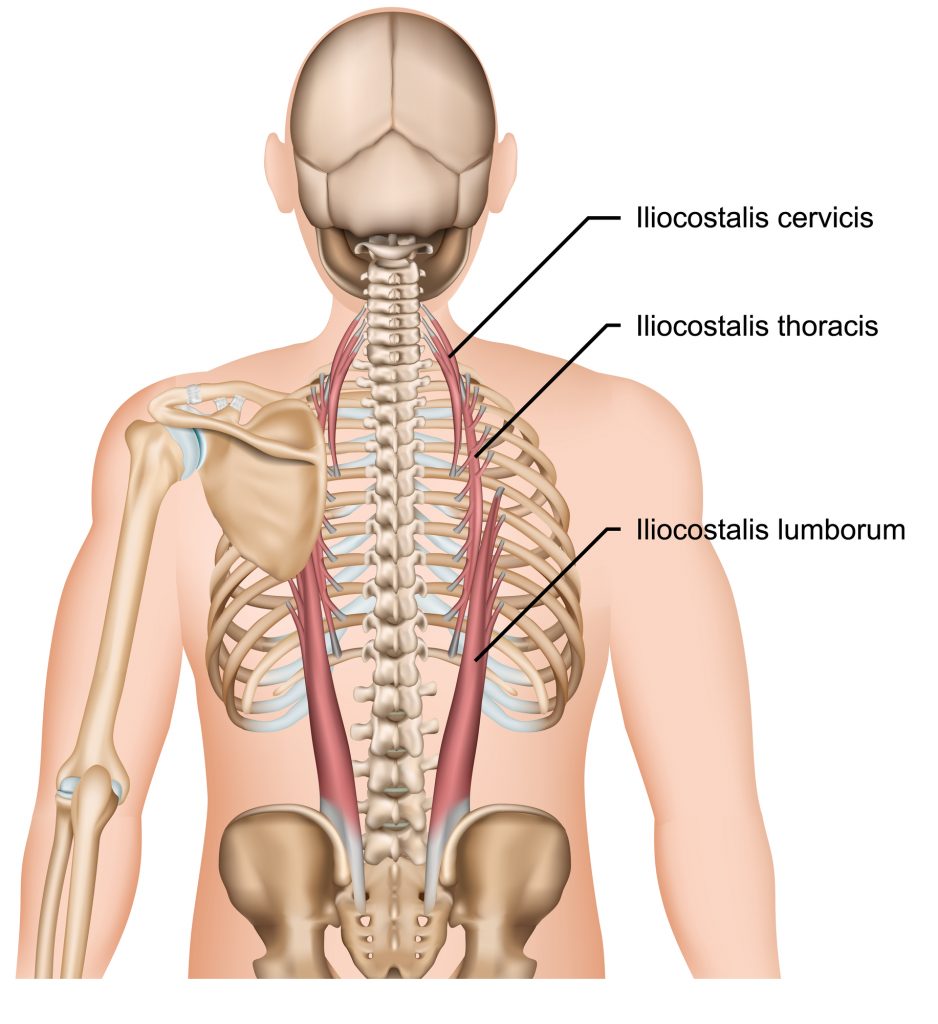
Function
The superficial ES extends the lumbar spine and helps stabilize the lower back.
Deep Erector Spinae
The deep ES is located beneath the superficial ES and above the multifidus. It attaches from the PSIS (posterior superior iliac spine) and iliac crest to the lumbar transverse processes.
Function
The deep ES has a small lever arm for extension. When the muscle contracts it squeezes the vertebrae together and dynamically checks anterior shear. Contraction of the deep ES also increases tension through the thoracolumbar fascia, contributing to stability of the lumbar spine.
Innervation
Dorsal rami of spinal nerves
Blood Supply
Dorsal branches of the lateral sacral and median sacral arteries.
FAQS
Spinal flexion with side bending away from the side being stretched is the most effective way to stretch this muscle group. To stretch the left ES you would flex the lumbar spine and side bend to the right. To stretch the right ES you wold flex the lumbar spine and side bend to the left.
A group of muscles running along either side of the spine. The muscles attache from the sacrum to the lumbar spine, thoracic spine, and ribs. The erector spinae musculature acts to extend the lumbar spine, check anterior shear forces, and stabilize the lumbar motion segments.
The muscles are located on the left and right sides of the spine. They attache from the sacrum and iliac crest to the lumbar transverse processes, ribs, and thoracic spine. The muscles span the entire length of the spinal column.
Spinal extension, side bending, checking anterior shear forces, stabilization of the lumbar spine.
Exercises that involve spinal extension will strengthen this muscle group. Spinal extension through a comfortable range with static holds in neutral are especially effective to strengthen the erector spinae musculature.

