A disc protrusion is a type of herniated disc where the part of the disc that is herniated beyond the normal disc space is smaller compared to the base of the herniation. The picture below depicts a disc protrusion.
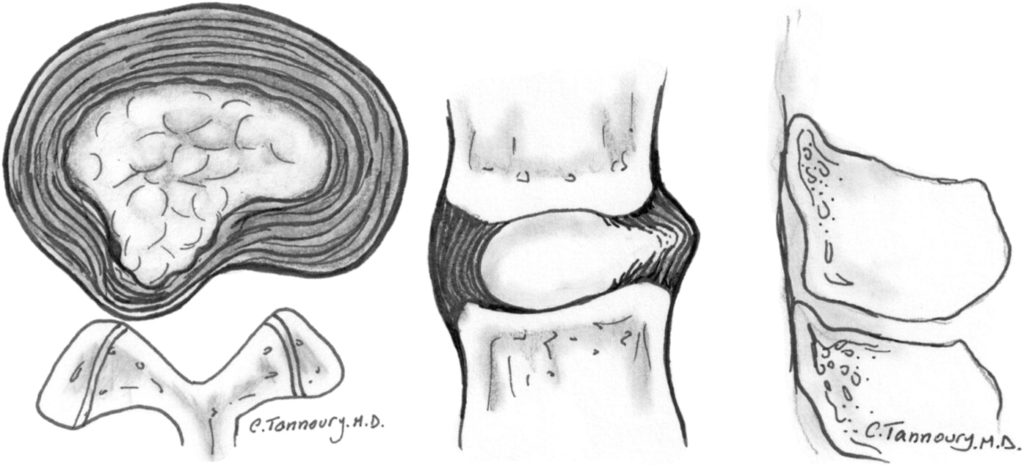
Normal Disc
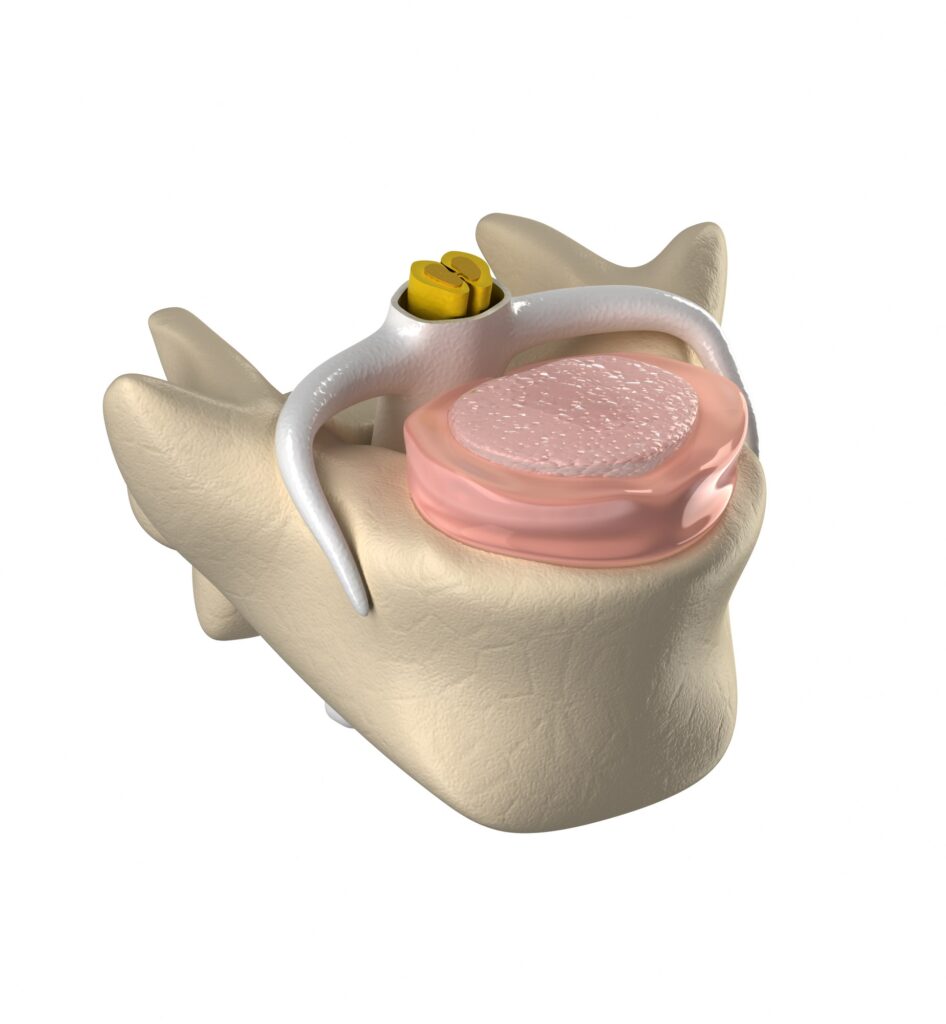
A disc protrusion may or may not be painful. Of note is the fact that just as many people WITHOUT low back pain have protruded discs compared to people WITH low back pain.
A disc protrusion may result in lower back pain, sciatica, or both. A disc protrusion may be asymptomatic.
When a disc protrusion is resulting in lower back pain or sciatica there are specific types of exercises that will decrease pain and other types of exercises that will exacerbate symptoms. Safe Exercises to do With a Herniated Disc covers what types of exercises will facilitate the healing process and what types of exercises to avoid.
FAQS
A type of herniated disc where the part of the disc that is herniated beyond the normal disc space is smaller compared to the base of the herniation.
A disc protrusion that is located beside the center of the disc. A paracentral disc protrusion will be a left or right protrusion, to the left or right of the center of the disc. Anatomically a paracentral protrusion occurs between the spinal cord and the intervertebral foramen, where the nerve root exits the spinal cord.
A central disc protrusion is located through the central part of the disc, when viewing the disc from above or below (through the transverse or axial plane). Anatomically a central disc protrusion reduces the space in the vertebral canal, around the spinal cord.
Disc protrusion refers to a type of herniated disc where the part of the disc that is herniated beyond the normal disc space is smaller compared to the base of the herniation.
Broad based disc protrusion describes the amount of protrusion that has occurred related to the circumference of the disc. A broad based disc protrusion involves 25% to 50% of the total circumference of the disc.
Disc protrusion is often the result of normal wear over time. As humans age the incidence of disc herniations and protrusions increase. Disc protrusion can be the result of acute injury as well. Repetitive lumbar flexion, lumbar flexion under load, and lumbar flexion with rotation (twisting) can cause disc protrusion.
References
Fardon DF, Williams AL, Dohring EJ, Murtagh FR, Gabriel Rothman SL, Sze GK. Lumbar disc nomenclature: version 2.0: Recommendations of the combined task forces of the North American Spine Society, the American Society of Spine Radiology and the American Society of Neuroradiology. Spine J. 2014 Nov 1;14(11):2525-45. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2014.04.022. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Review. PubMed PMID: 24768732.

